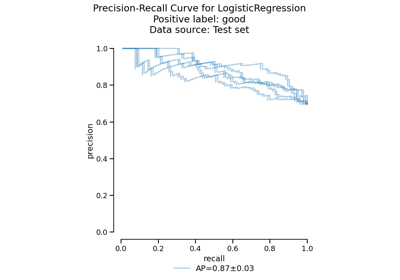
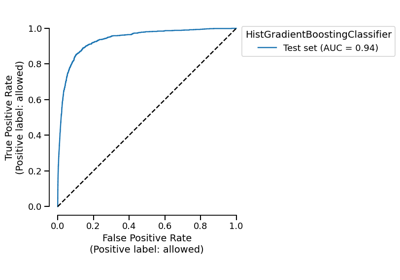
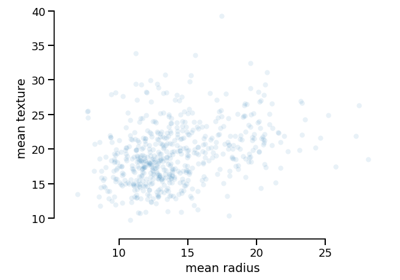
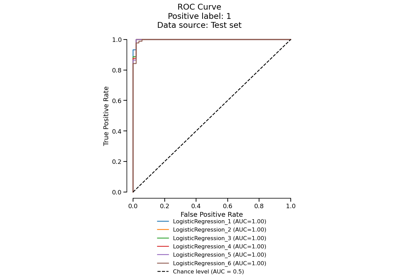
EstimatorReport#
- class skore.EstimatorReport(estimator, *, fit='auto', X_train=None, y_train=None, X_test=None, y_test=None, pos_label=None)[source]#
Report for a fitted estimator.
This class provides a set of tools to quickly validate and inspect a scikit-learn compatible estimator.
Refer to the Reporter for a single estimator section of the user guide for more details.
- Parameters:
- estimatorestimator object
Estimator to make the report from. When the estimator is not fitted, it is deep-copied to avoid side-effects. If it is fitted, it is cloned instead.
- fit{“auto”, True, False}, default=”auto”
Whether to fit the estimator on the training data. If “auto”, the estimator is fitted only if the training data is provided.
- X_train{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) or None
Training data.
- y_trainarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) or None
Training target.
- X_test{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) or None
Testing data. It should have the same structure as the training data.
- y_testarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) or None
Testing target.
- pos_labelint, float, bool or str, default=None
For binary classification, the positive class. If
Noneand the target labels are{0, 1}or{-1, 1}, the positive class is set to1. For other labels, some metrics might raise an error ifpos_labelis not defined.
- Attributes:
- estimator_estimator object
The cloned or copied estimator.
- estimator_name_str
The name of the estimator.
- fit_time_float or None
The time taken to fit the estimator, in seconds. If the estimator is not internally fitted, the value is
None.
See also
skore.CrossValidationReportReport of cross-validation results.
skore.ComparisonReportReport of comparison between estimators.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> X, y = make_classification(random_state=42) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=42, as_dict=True) >>> estimator = LogisticRegression() >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> report = EstimatorReport(estimator, **split_data)
- cache_predictions(response_methods='auto', n_jobs=None)[source]#
Cache estimator’s predictions.
- Parameters:
- response_methods“auto” or list of str, default=”auto”
The response methods to precompute. If “auto”, the response methods are inferred from the ml task: for classification we compute the response of the
predict_proba,decision_functionandpredictmethods; for regression we compute the response of thepredictmethod.- n_jobsint or None, default=None
The number of jobs to run in parallel. None means 1 unless in a joblib.parallel_backend context. -1 means using all processors.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=0, as_dict=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = EstimatorReport(classifier, **split_data) >>> report.cache_predictions() >>> report._cache {...}
- clear_cache()[source]#
Clear the cache.
Note that the cache might not be empty after this method is run as some values need to be kept, such as the fit time.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=0, as_dict=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = EstimatorReport(classifier, **split_data) >>> report.cache_predictions() >>> report.clear_cache() >>> report._cache {}
- get_predictions(*, data_source, response_method='predict', X=None, pos_label=<DEFAULT>)[source]#
Get estimator’s predictions.
This method has the advantage to reload from the cache if the predictions were already computed in a previous call.
- Parameters:
- data_source{“test”, “train”, “X_y”}, default=”test”
The data source to use.
“test” : use the test set provided when creating the report.
“train” : use the train set provided when creating the report.
“X_y” : use the provided
Xandyto compute the predictions.
- response_method{“predict”, “predict_proba”, “decision_function”}, default=”predict”
The response method to use to get the predictions.
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features), default=None
When
data_sourceis “X_y”, the input features on which to compute the response method.- pos_labelint, float, bool, str or None, default=_DEFAULT
The label to consider as the positive class when computing predictions in binary classification cases. By default, the positive class is set to the one provided when creating the report. If
None,estimator_.classes_[1]is used as positive label.When
pos_labelis equal toestimator_.classes_[0], it will be equivalent toestimator_.predict_proba(X)[:, 0]forresponse_method="predict_proba"and-estimator_.decision_function(X)forresponse_method="decision_function".
- Returns:
- np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_classes)
The predictions.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If the data source is invalid.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> X, y = make_classification(random_state=42) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=42, as_dict=True) >>> estimator = LogisticRegression() >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> report = EstimatorReport(estimator, **split_data) >>> predictions = report.get_predictions(data_source="test") >>> predictions.shape (25,)
Gallery examples#
EstimatorReport: Get insights from any scikit-learn estimator
train_test_split: get diagnostics when splitting your data
Using skore with scikit-learn compatible estimators
EstimatorReport: Inspecting your models with the feature importance