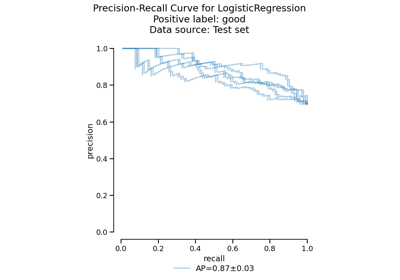
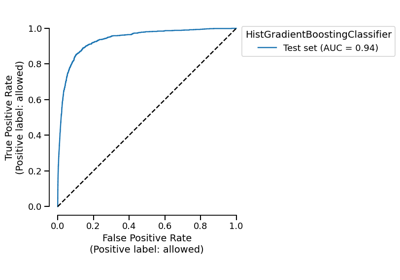
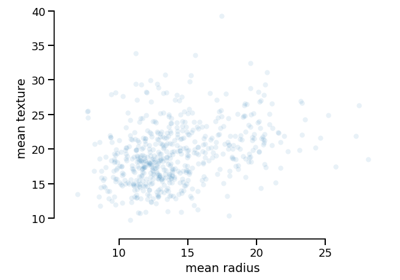
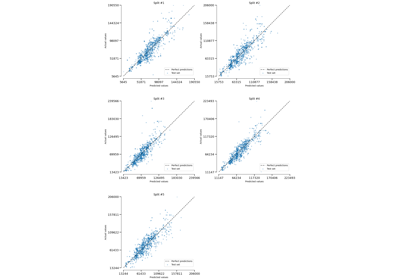
CrossValidationReport#
- class skore.CrossValidationReport(estimator, X, y=None, pos_label=None, splitter=None, n_jobs=None)[source]#
Report for cross-validation results.
Upon initialization,
CrossValidationReportwill cloneestimatoraccording tosplitterand fit the generated estimators. The fitting is done in parallel.Refer to the Cross-validation estimator section of the user guide for more details.
- Parameters:
- estimatorestimator object
Estimator to make the cross-validation report from.
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data to fit. Can be for example a list, or an array.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
The target variable to try to predict in the case of supervised learning.
- pos_labelint, float, bool or str, default=None
For binary classification, the positive class. If
Noneand the target labels are{0, 1}or{-1, 1}, the positive class is set to1. For other labels, some metrics might raise an error ifpos_labelis not defined.- splitterint, cross-validation generator or an iterable, default=5
Determines the cross-validation splitting strategy. Possible inputs for
splitterare:int, to specify the number of splits in a
(Stratified)KFold,a scikit-learn CV splitter,
An iterable yielding (train, test) splits as arrays of indices.
For int/None inputs, if the estimator is a classifier and
yis either binary or multiclass,StratifiedKFoldis used. In all other cases,KFoldis used. These splitters are instantiated withshuffle=Falseso the splits will be the same across calls.Refer to scikit-learn’s User Guide for the various cross-validation strategies that can be used here.
- n_jobsint, default=None
Number of jobs to run in parallel. Training the estimator and computing the score are parallelized over the cross-validation splits. When accessing some methods of the
CrossValidationReport, then_jobsparameter is used to parallelize the computation.Nonemeans 1 unless in ajoblib.parallel_backendcontext.-1means using all processors.
- Attributes:
- estimator_estimator object
The cloned or copied estimator.
- estimator_name_str
The name of the estimator.
- estimator_reports_list of EstimatorReport
The estimator reports for each split.
See also
skore.EstimatorReportReport for a fitted estimator.
skore.ComparisonReportReport of comparison between estimators.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> X, y = make_classification(random_state=42) >>> estimator = LogisticRegression() >>> from skore import CrossValidationReport >>> report = CrossValidationReport(estimator, X=X, y=y, splitter=2)
- cache_predictions(response_methods='auto', n_jobs=None)[source]#
Cache the predictions for sub-estimators reports.
- Parameters:
- response_methods{“auto”, “predict”, “predict_proba”, “decision_function”}, default=”auto”
The methods to use to compute the predictions.
- n_jobsint, default=None
The number of jobs to run in parallel. If
None, we use then_jobsparameter when initializingCrossValidationReport.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import CrossValidationReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = CrossValidationReport(classifier, X=X, y=y, splitter=2) >>> report.cache_predictions() >>> report._cache {...}
- clear_cache()[source]#
Clear the cache.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import CrossValidationReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = CrossValidationReport(classifier, X=X, y=y, splitter=2) >>> report.cache_predictions() >>> report.clear_cache() >>> report._cache {}
- create_estimator_report(*, X_test=None, y_test=None)[source]#
Create an estimator report from the cross-validation report.
This method creates a new
EstimatorReportwith the same estimator and the same data as the cross-validation report. It is useful to evaluate and deploy a model that was deemed optimal with cross-validation. Provide a held out test set to properly evaluate the performance of the model.- Parameters:
- X_test{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features) or None
Testing data. It should have the same structure as the training data.
- y_testarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs) or None
Testing target.
- Returns:
- report
EstimatorReport The estimator report.
- report
- get_predictions(*, data_source, response_method='predict', X=None, pos_label=<DEFAULT>)[source]#
Get estimator’s predictions.
This method has the advantage to reload from the cache if the predictions were already computed in a previous call.
- Parameters:
- data_source{“test”, “train”}, default=”test”
The data source to use.
“test” : use the test set provided when creating the report.
“train” : use the train set provided when creating the report.
“X_y” : use the train set provided when creating the report and the target variable.
- response_method{“predict”, “predict_proba”, “decision_function”}, default=”predict”
The response method to use to get the predictions.
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features), default=None
When
data_sourceis “X_y”, the input features on which to compute the response method.- pos_labelint, float, bool, str or None, default=_DEFAULT
The label to consider as the positive class when computing predictions in binary classification cases. By default, the positive class is set to the one provided when creating the report. If
None,estimator_.classes_[1]is used as positive label.When
pos_labelis equal toestimator_.classes_[0], it will be equivalent toestimator_.predict_proba(X)[:, 0]forresponse_method="predict_proba"and-estimator_.decision_function(X)forresponse_method="decision_function".
- Returns:
- list of np.ndarray of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_classes)
The predictions for each cross-validation split.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If the data source is invalid.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import make_classification >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> X, y = make_classification(random_state=42) >>> estimator = LogisticRegression() >>> from skore import CrossValidationReport >>> report = CrossValidationReport(estimator, X=X, y=y, splitter=2) >>> predictions = report.get_predictions(data_source="test") >>> print([split_predictions.shape for split_predictions in predictions]) [(50,), (50,)]