RocCurveDisplay#
- class skore.RocCurveDisplay(*, roc_curve, roc_auc, pos_label, data_source, ml_task, report_type)[source]#
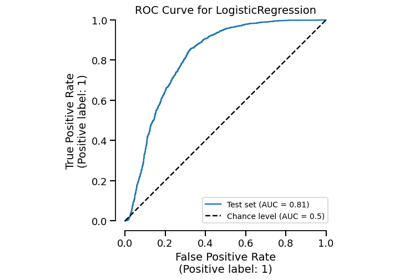
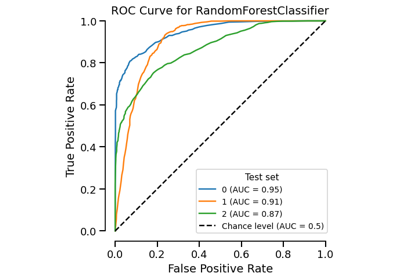
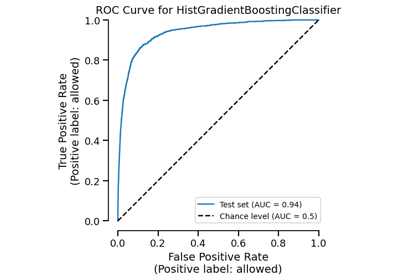
ROC Curve visualization.
An instance of this class should be created by
EstimatorReport.metrics.roc(). You should not create an instance of this class directly.- Parameters:
- roc_curveDataFrame
The ROC curve data to display. The columns are
estimator_namesplit(may be null)labelthresholdfprtpr.
- roc_aucDataFrame
The ROC AUC data to display. The columns are
estimator_namesplit(may be null)labelroc_auc.
- pos_labelint, float, bool, str or None
The class considered as positive. Only meaningful for binary classification.
- data_source{“train”, “test”, “X_y”}
The data source used to compute the ROC curve.
- ml_task{“binary-classification”, “multiclass-classification”}
The machine learning task.
- report_type{“comparison-cross-validation”, “comparison-estimator”, “cross-validation”, “estimator”}
The type of report.
- Attributes:
- ax_matplotlib axes or array of axes
The axes on which the ROC curve is plotted.
- figure_matplotlib figure
The figure on which the ROC curve is plotted.
- lines_list of matplotlib lines
The lines of the ROC curve.
- chance_level_matplotlib line or list of lines or None
The chance level line.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=0, as_dict=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = EstimatorReport(classifier, **split_data) >>> display = report.metrics.roc() >>> display.plot(roc_curve_kwargs={"color": "tab:red"})
- frame(with_roc_auc=False)[source]#
Get the data used to create the ROC curve plot.
- Parameters:
- with_roc_aucbool, default=False
Whether to include ROC AUC scores in the output DataFrame.
- Returns:
- DataFrame
A DataFrame containing the ROC curve data with columns depending on the report type:
estimator_name: Name of the estimator (when comparing estimators)split: Cross-validation split ID (when doing cross-validation)label: Class label (for multiclass-classification)threshold: Decision thresholdfpr: False Positive Ratetpr: True Positive Rateroc_auc: Area Under the Curve (whenwith_roc_auc=True)
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import EstimatorReport, train_test_split >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=0, as_dict=True) >>> clf = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = EstimatorReport(clf, **split_data) >>> display = report.metrics.roc() >>> df = display.frame()
- plot(*, estimator_name=None, roc_curve_kwargs=None, plot_chance_level=True, chance_level_kwargs=None, despine=True)[source]#
Plot visualization.
Extra keyword arguments will be passed to matplotlib’s
plot.- Parameters:
- estimator_namestr, default=None
Name of the estimator used to plot the ROC curve. If
None, we use the inferred name from the estimator.- roc_curve_kwargsdict or list of dict, default=None
Keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib’s
plotfor rendering the ROC curve(s).- plot_chance_levelbool, default=True
Whether to plot the chance level.
- chance_level_kwargsdict, default=None
Keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib’s
plotfor rendering the chance level line.- despinebool, default=True
Whether to remove the top and right spines from the plot.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer >>> from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression >>> from skore import train_test_split >>> from skore import EstimatorReport >>> X, y = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True) >>> split_data = train_test_split(X=X, y=y, random_state=0, as_dict=True) >>> classifier = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10_000) >>> report = EstimatorReport(classifier, **split_data) >>> display = report.metrics.roc() >>> display.plot(roc_curve_kwargs={"color": "tab:red"})
- set_style(**kwargs)[source]#
Set the style parameters for the display.
- Parameters:
- **kwargsdict
Style parameters to set. Each parameter name should correspond to a a style attribute passed to the plot method of the display.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Returns the instance itself.
- Raises:
- ValueError
If a style parameter is unknown.
Gallery examples#
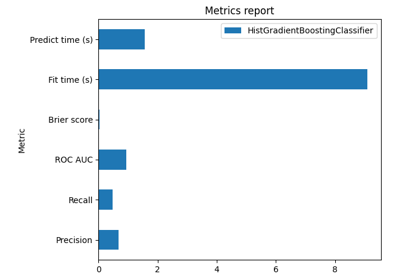
EstimatorReport: Get insights from any scikit-learn estimator