Visualization via the skore display API#
skore provides a family of objects that we call displays. All displays follow the
common API defined by the Display protocol. As a user, you get a display by
interacting with a reporter. Let’s provide an example:
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from skore import CrossValidationReport
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=10_000,
n_classes=3,
class_sep=0.3,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
random_state=42,
)
report = CrossValidationReport(LogisticRegression(), X, y)
display = report.metrics.roc()
display.plot()
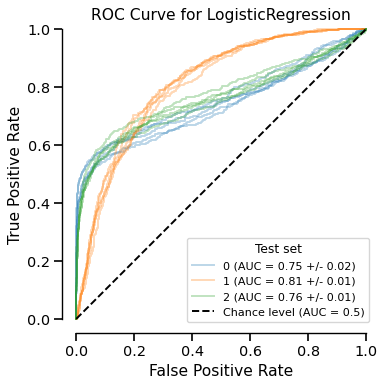
The EstimatorReport.metrics.roc() creates a RocCurveDisplay object.
The help method displays the available attributes and methods of the
display object interactively:
display.help()
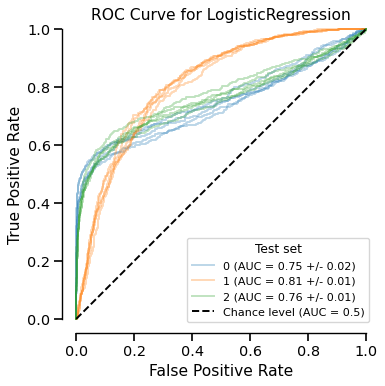
Another available method is plot. It shows graphically
the information contained in the display. Call it as many times as you want - it does
not modify the display object nor require heavy computation.
display.plot()
The plot method can be preceded by the set_style method which accepts parameters to
tweak the rendering of the display. For instance, customize the appearance of the chance level:
display.set_style(
chance_level_kwargs=dict(linestyle="-", linewidth=5, color="tab:purple")
)
display.plot()
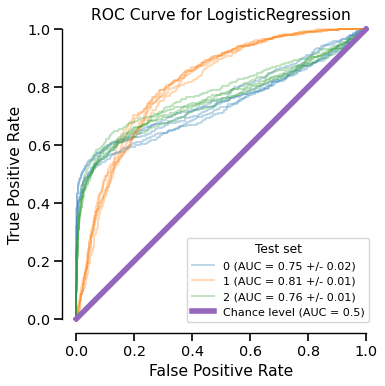
Any subsequent call to plot uses the style settings set by set_style.
The frame method retrieves the underlying data used to generate the plot as a
pandas.DataFrame:
df = display.frame()
df.head()