Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Quick start#
Machine learning evaluation and diagnostics#
Evaluate your model using skore’s CrossValidationReport:
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from skore import CrossValidationReport
X, y = make_classification(n_classes=2, n_samples=100_000, n_informative=4)
clf = LogisticRegression()
cv_report = CrossValidationReport(clf, X, y)
Display the help tree to see all the insights that are available to you (skore detected that you are doing binary classification):
╭─────────────────── Tools to diagnose estimator LogisticRegression ───────────────────╮
│ CrossValidationReport │
│ ├── .metrics │
│ │ ├── .accuracy(...) (↗︎) - Compute the accuracy score. │
│ │ ├── .brier_score(...) (↘︎) - Compute the Brier score. │
│ │ ├── .log_loss(...) (↘︎) - Compute the log loss. │
│ │ ├── .precision(...) (↗︎) - Compute the precision score. │
│ │ ├── .precision_recall(...) - Plot the precision-recall curve. │
│ │ ├── .recall(...) (↗︎) - Compute the recall score. │
│ │ ├── .roc(...) - Plot the ROC curve. │
│ │ ├── .roc_auc(...) (↗︎) - Compute the ROC AUC score. │
│ │ ├── .timings(...) - Get all measured processing times related │
│ │ │ to the estimator. │
│ │ ├── .custom_metric(...) - Compute a custom metric. │
│ │ └── .report_metrics(...) - Report a set of metrics for our estimator. │
│ ├── .cache_predictions(...) - Cache the predictions for sub-estimators │
│ │ reports. │
│ ├── .clear_cache(...) - Clear the cache. │
│ ├── .get_predictions(...) - Get estimator's predictions. │
│ └── Attributes │
│ ├── .X - The data to fit │
│ ├── .y - The target variable to try to predict in │
│ │ the case of supervised learning │
│ ├── .estimator_ - The cloned or copied estimator │
│ ├── .estimator_name_ - The name of the estimator │
│ ├── .estimator_reports_ - The estimator reports for each split │
│ └── .n_jobs - Number of jobs to run in parallel │
│ │
│ │
│ Legend: │
│ (↗︎) higher is better (↘︎) lower is better │
╰──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
Display the report metrics that was computed for you:
df_cv_report_metrics = cv_report.metrics.report_metrics(pos_label=1)
df_cv_report_metrics
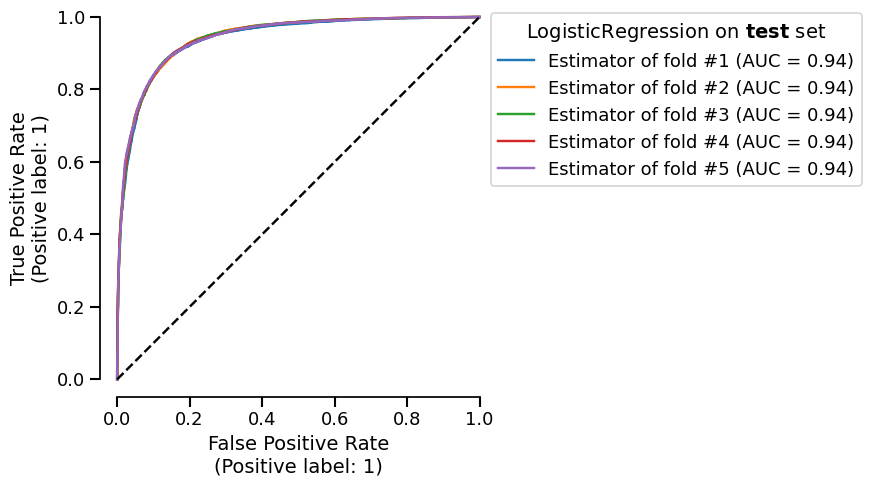
Display the ROC curve that was generated for you:
roc_plot = cv_report.metrics.roc()
roc_plot.plot()
Skore project: storing some items#
From your Python code, create and load a skore Project:
import skore
my_project = skore.Project("my_project")
This will create a skore project directory named my_project.skore in your
current working directory.
Store some previous results in the skore project for safe-keeping:
my_project.put("df_cv_report_metrics", df_cv_report_metrics)
my_project.put("roc_plot", roc_plot)
Retrieve what was stored:
df_get = my_project.get("df_cv_report_metrics")
df_get
See also
For a more in-depth guide, see our Skore: getting started page!
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.481 seconds)